Your cart is currently empty!
Google Tag Manager Server-Side Tagging: Do I Really Need It?
- What is Google Tag Manager?
- Understanding Tagging
- Client-Side Tagging
- Server-Side Tagging
- Tealium and Early Server-Side Tagging
- Pros and Cons of Server-Side Tagging in GTM
- Misconceptions About Server-Side Tagging
- Do You Really Need Server-Side Tagging?
- Implementation of Server-Side Tagging in GTM
- FAQs
- What is the main difference between client-side and server-side tagging?
- Can small businesses benefit from server-side tagging?
- Does server-side tagging eliminate the impact of ad blockers?
- Is server-side tagging more secure than client-side tagging?
- What are the cost implications of server-side tagging?
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a free tool provided by Google that allows marketers and developers to manage and deploy marketing tags (snippets of code or tracking pixels) on their websites without modifying the site code directly. GTM streamlines the process of tag management, enabling users to easily update and handle tags through an intuitive interface. This flexibility reduces the dependency on developers for minor tag updates and empowers marketers to make real-time changes.
Understanding Tagging
Tags are small pieces of code embedded in a website to collect data and send it to various analytics and marketing platforms. These tags can track user behavior, measure conversions, and gather other valuable metrics. For instance, Google Analytics tags can provide insights into user interactions on a website, while AdWords conversion tracking tags can measure the effectiveness of ad campaigns.
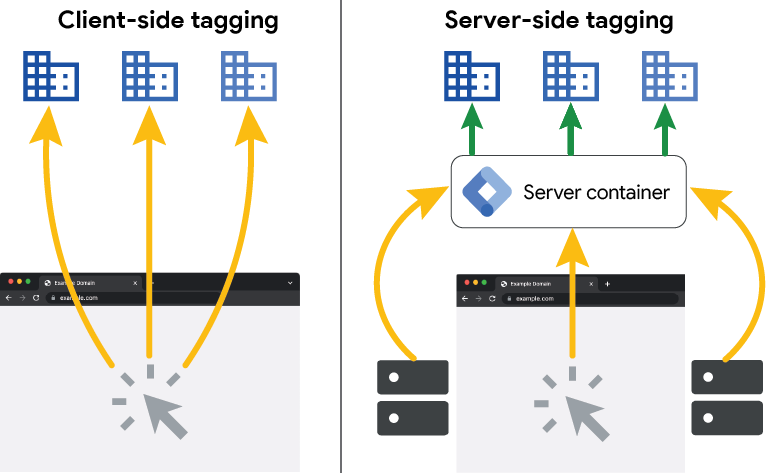 Client-Side Tagging
Client-Side Tagging
Definition and Basic Concept
Client-side tagging involves placing tags directly within the user’s browser. When a user visits a website, their browser executes the tags, which then send data to the respective third-party servers. This method has been the standard practice in web analytics and marketing for many years.
How Client-Side Tagging Works
In client-side tagging, tags are embedded in the HTML of a webpage. When the page loads, the browser runs the tags, collecting data such as page views, clicks, and other user interactions. This data is then sent directly from the browser to the analytics or marketing platforms.
Advantages of Client-Side Tagging
- Ease of Implementation: Adding and modifying tags is straightforward, often requiring minimal technical knowledge.
- Immediate Data Collection: Data is collected in real-time as users interact with the website, providing instant insights.
- Broad Compatibility: Most marketing and analytics platforms support client-side tagging, making it widely accessible.
Disadvantages of Client-Side Tagging
- Performance Impact: Multiple tags can slow down page load times, negatively affecting the user experience.
- Ad Blockers: Tags can be blocked by ad blockers, resulting in incomplete data collection.
- Data Privacy Concerns: User data is exposed to third parties, which can raise privacy and compliance issues.
Server-Side Tagging
Definition and Basic Concept
Server-side tagging involves processing tags on the server rather than the user’s browser. This approach shifts the burden of tag execution from the client to the server, providing better control over data handling and security.
How Server-Side Tagging Works
In server-side tagging, a server processes the tags and sends the necessary data to third-party endpoints. The user’s browser sends a single request to the server, which then handles all tag-related activities. This reduces the load on the user’s browser and improves data privacy by masking user information before it is sent to third parties.
Advantages of Server-Side Tagging
- Performance Improvements: Offloading tag processing to the server reduces the strain on the browser, resulting in faster page loads.
- Data Accuracy: Server-side tagging minimizes data loss caused by ad blockers and browser limitations, ensuring more reliable data collection.
- Security and Privacy: By controlling data transmission from the server, businesses can enhance user privacy and comply more easily with data protection regulations.
Disadvantages of Server-Side Tagging
- Technical Complexity: Setting up and maintaining server-side tagging requires more technical expertise and resources.
- Higher Costs: There may be additional costs associated with server resources and ongoing maintenance.
- Implementation Challenges: The initial setup can be complex, especially for businesses without dedicated IT teams.
Tealium and Early Server-Side Tagging
Tealium, a pioneer in the tag management space, introduced server-side tagging long before it became popular with GTM. Tealium’s approach offered enhanced performance and data privacy, setting a benchmark for other platforms. By processing tags on the server, Tealium provided a solution that reduced the load on user browsers and improved data security.
Comparison Between Tealium and GTM’s Server-Side Tagging
- Performance: Both platforms offer improved performance by processing tags on the server, leading to faster page loads.
- Data Privacy: Tealium has been known for its robust privacy features, which GTM now also offers through server-side tagging.
- Technical Requirements: Both require a higher level of technical expertise compared to client-side tagging, though GTM’s widespread use and integration with other Google services make it a popular choice.
Pros and Cons of Server-Side Tagging in GTM
Server-side tagging in GTM brings several benefits but also comes with its own set of challenges.
Pros
- Performance Improvements: By shifting the load from the client to the server, websites can achieve faster load times, enhancing the user experience.
- Data Accuracy: Server-side tagging ensures more accurate data collection by reducing the impact of ad blockers and browser limitations.
- Enhanced Security: With better control over data transmission, businesses can improve user privacy and comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Flexibility: Server-side tagging offers greater flexibility in how data is processed and transmitted to third-party platforms, allowing for more sophisticated data handling.
Cons
- Technical Complexity: Implementing server-side tagging requires significant technical expertise, which can be a barrier for smaller businesses.
- Higher Costs: The need for server resources and ongoing maintenance can lead to higher costs compared to client-side tagging.
- Implementation Challenges: Setting up server-side tagging can be complex, requiring a detailed understanding of both the technical and business aspects of data collection.
Misconceptions About Server-Side Tagging
There are several misconceptions about server-side tagging that need to be addressed.
Myth 1: Server-Side Tagging is Only for Large Enterprises
While it’s true that larger enterprises often have the resources to implement server-side tagging, smaller businesses can also benefit from it. The key is to weigh the benefits against the costs and technical requirements.
Myth 2: Server-Side Tagging Completely Eliminates Ad Blockers
Server-side tagging can reduce the impact of ad blockers, but it doesn’t eliminate them entirely. Some ad blockers can still detect and block server-side requests, though the overall data loss is significantly reduced.
Myth 3: Server-Side Tagging is Too Complicated to Implement
Although server-side tagging is more complex than client-side tagging, many platforms, including GTM, provide comprehensive guides and support to help businesses implement it successfully.
Do You Really Need Server-Side Tagging?
The decision to implement server-side tagging depends on various factors, including your business size, technical capabilities, and specific needs.
Factors to Consider
- Performance Requirements: If your website suffers from slow load times due to client-side tags, server-side tagging can help improve performance.
- Data Accuracy Needs: For businesses that rely heavily on accurate data collection, server-side tagging can offer a more reliable solution.
- Privacy and Compliance: If data privacy and regulatory compliance are major concerns, server-side tagging provides better control over data transmission.
Scenarios Where Server-Side Tagging is Beneficial
- High Traffic Websites: Websites with high traffic volumes can benefit from the performance improvements offered by server-side tagging.
- Privacy-Focused Businesses: Companies that prioritize user privacy and need to comply with strict data protection regulations will find server-side tagging advantageous.
- Complex Data Requirements: Businesses with complex data needs that require sophisticated data processing and integration will benefit from the flexibility of server-side tagging.
Scenarios Where Client-Side Tagging is Sufficient
- Small to Medium Businesses: For smaller businesses with limited technical resources, client-side tagging may be sufficient.
- Simple Data Collection: If your data collection needs are straightforward and you don’t face significant performance issues, client-side tagging can still be effective.
Implementation of Server-Side Tagging in GTM
Implementing server-side tagging in GTM involves several steps. Here is a simplified guide to get you started:
- Set Up a Server-Side Container: In GTM, create a new server-side container. This container will handle the processing of tags on the server.
- Configure Your Server: Set up a server to host the server-side container. Google provides options for deploying on Google Cloud Platform, but you can also use other hosting providers.
- Migrate Tags to the Server-Side Container: Move your existing tags from the client-side container to the server-side container. This may involve adjusting tag configurations to work with server-side processing.
- Update Your Website: Modify your website to send data to the server-side container instead of the client-side container. This often involves updating tracking codes and other data collection mechanisms.
- Test and Validate: Thoroughly test the server-side tagging setup to ensure data is collected accurately and the performance benefits are realized.
FAQs
What is the main difference between client-side and server-side tagging?
Client-side tagging processes tags in the user’s browser, while server-side tagging processes them on a server. This shift can improve performance, data accuracy, and security.
Can small businesses benefit from server-side tagging?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from server-side tagging, especially if they face performance issues or have stringent data privacy requirements. However, they need to consider the technical and cost implications.
Does server-side tagging eliminate the impact of ad blockers?
Server-side tagging reduces the impact of ad blockers on data collection, but it does not eliminate it entirely. Some ad blockers can still detect and block server-side requests.
Is server-side tagging more secure than client-side tagging?
Yes, server-side tagging provides better control over data transmission, enhancing security and privacy. It allows businesses to mask user data before sending it to third parties.
What are the cost implications of server-side tagging?
Server-side tagging can involve additional costs for server resources, maintenance, and potentially higher technical support. Businesses need to weigh these costs against the benefits.



