Your cart is currently empty!
How Many Websites Use Google Analytics?
- From Server Logs to Cross Device Tracking With Google Analytics: The Evolution of Web Analytics and its Impact on Digital Marketing
- The Growth of Google Analytics: A Decade of Evolution and Impact on Digital Marketing
- Popularity and Industry Impact
- Google Analytics Across Industries: Tracking Trends and Optimizing Performance
- Distribution of Websites Using Google Analytics by Implementation Method
- Author’s Final Words
Launched in 2005, revolutionized web analytics by offering robust, user-friendly tracking capabilities for free. Initially, its adoption was rapid among early adopters in the tech and marketing sectors. Over the years, its feature set expanded, incorporating advanced analytics, real-time reporting, and integration with other Google services such as Google Ads and Search Console.
From Server Logs to Cross Device Tracking With Google Analytics: The Evolution of Web Analytics and its Impact on Digital Marketing
The evolution of web analytics has been a fascinating journey for many professionals (including myself) who stepped into a new brand new hybrid space between marketing and web development, marked by significant milestones that have shaped the way we understand and utilize data in the digital world. It all began with server log analysis, which involved examining the logs generated by web servers to understand visitor behavior. This method provided basic insights such as the number of visitors, pages visited, and the duration of visits.
However, server log analysis had limitations, such as the inability to track individual user interactions and the reliance on server-side data only. This led to the development of JavaScript-based analytics, which enabled tracking user interactions on the client side. One of the most significant players in this evolution was Google Analytics, which was launched in 2005.
GA for short, revolutionized web analytics by providing a free, easy-to-use platform that allowed website owners to track a wide range of metrics, including traffic sources, user demographics, and behavior. Its integration with Google’s other services, such as AdWords, further enhanced its appeal to marketers and website owners.
The introduction of Google Analytics marked a turning point in the growth of digital analytics for marketing. It provided marketers with powerful insights into the effectiveness of their campaigns, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and optimize their strategies for better results. Its user-friendly interface and robust feature set also helped democratize analytics, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Since then, web analytics has continued to evolve, driven by advancements in technology and the growing importance of data in digital marketing. Today, web analytics encompasses a wide range of tools and techniques, including heatmaps, session replay, and advanced data visualization, all aimed at providing deeper insights into user behavior and improving the overall digital experience.
The Growth of Google Analytics: A Decade of Evolution and Impact on Digital Marketing
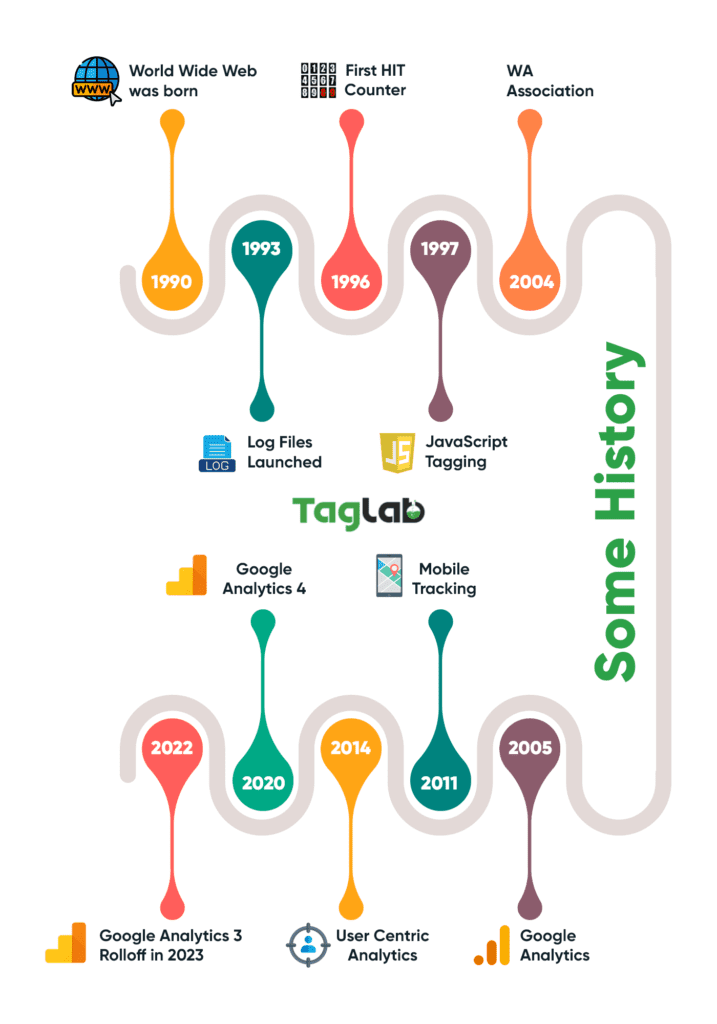
 Over the past two decades, web analytics has evolved from simple server log analysis to sophisticated tools like Google Analytics, reshaping how businesses understand and engage with their online audiences. Google Analytics, launched in 2005, quickly became a cornerstone of digital marketing, offering unprecedented insights into website performance and user behavior. As we delve into its evolution from 2005 to 2024, we witness how Google Analytics has not only transformed itself but also played a pivotal role in the broader narrative of digital analytics and marketing.
Over the past two decades, web analytics has evolved from simple server log analysis to sophisticated tools like Google Analytics, reshaping how businesses understand and engage with their online audiences. Google Analytics, launched in 2005, quickly became a cornerstone of digital marketing, offering unprecedented insights into website performance and user behavior. As we delve into its evolution from 2005 to 2024, we witness how Google Analytics has not only transformed itself but also played a pivotal role in the broader narrative of digital analytics and marketing.
- 2005-2010: Google Analytics quickly gained traction, reaching millions of users within the first few years. Its ease of use and integration with Google’s ecosystem made it a go-to tool for webmasters and marketers.
- 2011-2015: The introduction of Universal Analytics in 2012 brought enhanced tracking capabilities, which further boosted its adoption. By 2015, Google Analytics was used by tens of millions of websites globally.
- 2016-2020: During this period, the rise of digital transformation and the increasing importance of data-driven decision-making led to a significant increase in adoption. By 2020, over 50 million websites were using Google Analytics.
- 2021-2024: The launch of Google Analytics 4 (GA4) in 2020 marked another milestone, offering advanced machine learning capabilities and improved tracking of user journeys across devices and platforms. This new version continued to drive adoption, bringing the total to approximately 75 million websites by 2024.
Popularity and Industry Impact
Google Analytics is widely used across various industries due to its comprehensive features and flexibility. It helps businesses of all sizes gain insights into website traffic, user behavior, and marketing effectiveness. Its popularity can be attributed to several factors:
- Integration with Google Ecosystem: Seamless integration with Google Ads, Search Console, and other services makes it a powerful tool for marketers.
- Free and Accessible: Google Analytics offers a robust free version, making it accessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
- Advanced Features: With capabilities like real-time reporting, customizable dashboards, and AI powered insights, it caters to both beginners and advanced users.
- Community and Support: A large community of users, extensive documentation, and a range of tutorials and courses help users maximize the tool’s potential.
Google Analytics Across Industries: Tracking Trends and Optimizing Performance
Google Analytics is widely used across industries to gain insights into online user behavior and website performance. Its adoption varies significantly, reflecting the diverse needs and priorities of businesses in different sectors. For example, e-commerce websites utilize it to track conversions and optimize sales funnels, while media and publishing companies rely on it to understand reader engagement patterns. In the technology sector, GA helps track user interactions with products, aiding in the refinement of digital marketing strategies. Education websites analyze user engagement with course materials, while travel and hospitality sectors monitor booking patterns. Healthcare websites track patient interactions, and financial institutions use Google Analytics to optimize online services. Other industries, including government, non-profits, and personal blogs, also find utility in it for purposes such as performance tracking and audience analysis. This varied adoption underscores the tool’s versatility and value in providing actionable insights for businesses across diverse sectors.
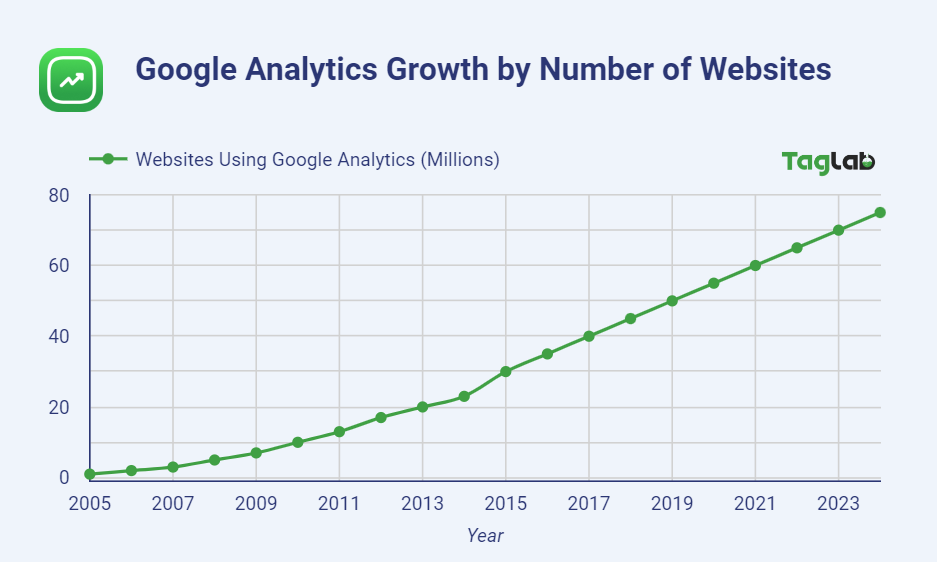
 E-commerce & Product: Approximately 32% the websites using Google Analytics are e-commerce related websitesbsites, utilizing it to track user behavior, monitor conversions, and optimize their sales funnel.
E-commerce & Product: Approximately 32% the websites using Google Analytics are e-commerce related websitesbsites, utilizing it to track user behavior, monitor conversions, and optimize their sales funnel.- Media and Publishing: Around 18% of websites using Google Analytics are in the media and publishing industry, utilizing it to understand reader engagement, popular content, and audience demographics.
- Technology: Roughly 15% of websites on Google Analytics are tech companies interested to measure the performance of their websites, track user interactions with products, and refine their digital marketing strategies.
- Education: About 12% of educational websites use Google Analytics to analyze user engagement with course materials, track student progress, and improve the overall user experience.
- Travel and Hospitality: Approximately 8% of websites using Google Analytics are in the travel and hospitality sector, interested in understanding booking patterns, monitor website traffic, and enhance their online booking process.
- Healthcare: Around 7% of website using Google Analytics are in the healthcare industry, potentially interested in tracking patient interactions, analyzing the effectiveness of health campaigns, and improving online appointment scheduling.
- Finance: Roughly 5% of Google Analytics website are financial institutions, with the objective to monitor user interactions on their websites, track conversions, and optimize their online services.
- Others: This category includes approximately the remaining 3% of websites from various industries like government, non-profits, and personal blogs that use Google Analytics for a range of purposes, including performance tracking, audience analysis, and content optimization.
Distribution of Websites Using Google Analytics by Implementation Method
GA is a widely used tool for website analytics, with varying methods employed for its implementation. Understanding these methods provides insight into web development practices. Here, we outline the three primary methods: Tag Management Systems (TMS), Script Injection in Source Code, and Third Party Tools Integration.
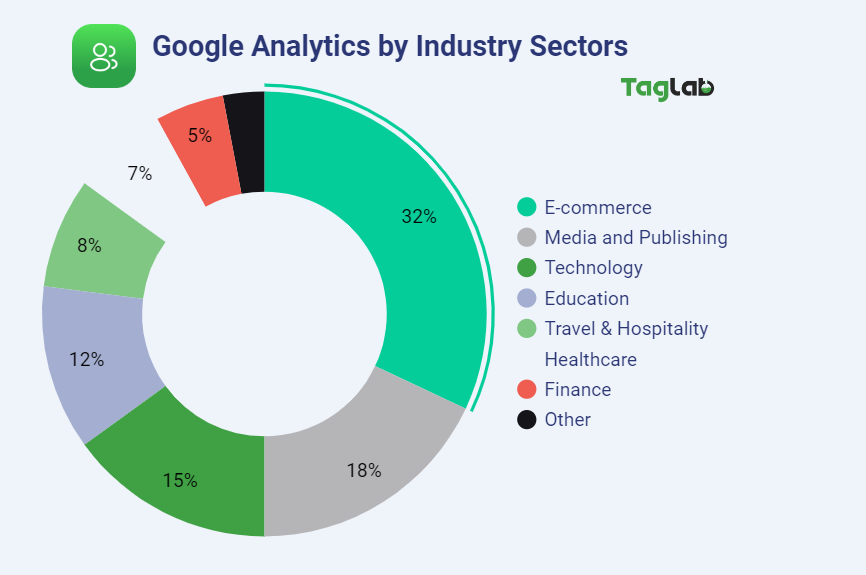
- Tag Management Systems (TMS): Around 60% of websites use TMS platforms like Google Tag Manager to implement Google Analytics. TMS allows for easy management and deployment of tags.
- Script Injection in Source Code: Approximately 30% of websites choose to manually insert the Google Analytics tracking code directly into their website’s source code. This method offers more control but requires technical expertise.
- Third Party Tools Integration: Roughly 10% of content management systems (CMS) and other web and marketing platforms offer native integration with Google Analytics. This allows users to easily add the tracking code without the need for manual implementation.
Author’s Final Words
Google Analytics has long been the market leader in digital analytics, offering a powerful and user-friendly platform for website owners to track and analyze their online performance. However, the digital landscape has evolved significantly in recent years, with the emergence of new privacy regulations and the growing demand for more robust analytics tools.
One of Google Analytics’ key strengths is its freemium model, which has helped drive its widespread adoption. By offering a free version of the tool, Google has been able to attract a large user base and establish itself as a leader in the digital analytics space. This freemium model has also helped bolster Google’s main business model, advertising services, by providing valuable data insights to advertisers.
Despite its strengths, Google Analytics is not without its challenges. The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and businesses are now faced with the need to navigate complex privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. These regulations place strict limitations on the collection and use of personal data, forcing businesses to rethink their analytics strategies and adopt more privacy-conscious tools. Additionally the launch of Google Analytics 4 have recieved several severe critics from the industry experts.
Furthermore, the demand for more robust analytics tools is also growing. As businesses seek to gain deeper insights into their online performance, they are looking for tools that offer more advanced features and capabilities. This has led to the emergence of new players in the digital analytics market, offering innovative solutions that cater to the evolving needs of businesses.
In conclusion, while Google Analytics remains a powerful tool for website analytics, the industry is evolving rapidly. Businesses are now faced with the challenge of navigating complex privacy regulations and the demand for more advanced analytics tools. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the key to success lies in adopting a holistic approach to analytics, leveraging a combination of tools and strategies to gain deeper insights and drive business growth.
Data collection methodology and disclaimer: The data presented in this article are estimations derived from rigorous analyses and business intelligence methods based on complex, multifaceted inputs. Part of the process involves scraping the public web with TAGLAB technology for reasearch purposes. Our data estimations are subject to inherent uncertainties stemming from the intricacies of the analytical methodologies employed, the diverse nature of the data sources utilized, and the dynamic nature of the phenomena under study. As such, these estimations are intended to serve as informed approximations rather than definitive values. The complexities inherent in the analytical process underscore the necessity for judicious interpretation and acknowledgment of the inherent limitations associated with such estimations.