Your cart is currently empty!
Marketing Attribution for E-commerce: Best Practices and Tools
- Why Attribution Matters for E-commerce
- Key Attribution Challenges in E-commerce
- Best Practices for Effective Marketing Attribution
- Top Tools for Marketing Attribution in E-commerce
- Measuring the Impact of Marketing Attribution
- Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Future Trends in Marketing Attribution for E-commerce
- Final Words
- Frequently Asked Questions
For instance, consider a scenario where a potential customer first learns about your product through a Facebook ad, signs up for your newsletter after reading a blog post, and eventually makes a purchase after clicking on an email promotion. Which channel gets credit for the sale? Without attribution, you might mistakenly attribute the entire conversion to the last interaction (the email), overlooking the significant role played by the Facebook ad and blog post. Marketing attribution solves this by mapping out the entire customer journey and distributing credit accordingly, giving you a holistic view of your marketing performance.
 Why Attribution Matters for E-commerce
Why Attribution Matters for E-commerce
Accurate attribution is critical for e-commerce businesses because it provides clarity on what’s working and what isn’t. With a deeper understanding of how different channels contribute to conversions, businesses can allocate their marketing budget more effectively, ensuring that the channels driving the most value receive the resources they need to thrive.
For example, an e-commerce store might invest heavily in paid ads, assuming they’re the primary driver of sales. However, attribution might reveal that organic search and social media are the real power players, with paid ads serving more as reminders than the primary point of engagement. With this insight, the business could reallocate part of its paid ad budget into SEO and social media strategies, potentially increasing the overall return on investment (ROI).
Moreover, by analyzing how various marketing efforts contribute to customer acquisition and retention, e-commerce businesses can optimize their campaigns for each stage of the buyer’s journey. This enables more personalized and targeted strategies, leading to better user experiences and, ultimately, higher conversion rates. Whether you’re focusing on acquiring new customers or nurturing existing ones, accurate attribution ensures that you’re investing in the right channels to achieve your specific goals.
Purpose of the Article
The purpose of this article is to provide e-commerce businesses with a comprehensive guide to implementing effective marketing attribution strategies. We’ll delve into best practices that help ensure accurate attribution, explore the various tools available for tracking and analyzing marketing performance, and address common challenges that businesses face. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how to leverage attribution data to make informed marketing decisions, optimize your campaigns, and ultimately, drive more revenue for your e-commerce store.
Key Attribution Challenges in E-commerce
Marketing attribution can be highly complex in the e-commerce space due to the variety of ways consumers interact with brands. Tracking these interactions accurately across multiple devices, channels, and even offline touchpoints is a significant challenge for businesses looking to make data-driven marketing decisions. Below are some of the most common attribution challenges faced by e-commerce businesses and insights into how these issues affect attribution accuracy.
Multi-Device and Multi-Channel Journeys
One of the biggest challenges in e-commerce attribution is tracking users who engage with your brand across different devices and channels. Consumers today rarely stick to one platform or device throughout their buying journey. A customer might first browse products on a smartphone, sign up for an email newsletter on a desktop, and later make a purchase via a tablet. This fragmented journey makes it difficult to connect the dots and accurately assign credit to each touchpoint.
In such multi-device journeys, attribution tools often struggle to unify the data, resulting in incomplete or inaccurate tracking. For example, a consumer may click on a paid social media ad from their mobile phone but later complete the purchase on a desktop after searching for the product again through organic search. Without a system that can link these touchpoints to the same user, you risk underreporting the value of the initial paid ad and over-crediting the final organic search click.
To overcome this, businesses need to adopt sophisticated attribution tools that allow cross-device tracking, giving them a more complete picture of the customer’s journey. Additionally, integrating these tools with customer profiles or user IDs can help bridge the gap between device-specific interactions and create a unified view of the buyer’s path.
Attribution Gaps in Data
Another common issue in e-commerce attribution is the presence of data silos and incomplete tracking mechanisms. With customers interacting with brands across numerous platforms—social media, email, paid search, and even third-party marketplaces—it can be difficult to consolidate all the data into one coherent view.
Many businesses use separate platforms for different marketing efforts, and these tools may not share data seamlessly. For instance, if your email marketing tool isn’t integrated with your CRM or website analytics platform, you might miss out on crucial insights, such as whether a customer who clicked on an email later made a purchase via your website. These data silos result in gaps that can distort attribution models and lead to inaccurate conclusions about which channels are driving sales.
Incomplete tracking also arises when businesses fail to properly implement tracking codes, such as UTM parameters or conversion tags, across their marketing channels. Without consistent tracking in place, even seemingly minor issues like untagged email links or broken conversion tracking pixels can lead to large attribution errors. As a result, businesses may misallocate their marketing budget or miss opportunities to refine underperforming campaigns.
To address this, e-commerce businesses should focus on integrating their data sources and implementing comprehensive tracking mechanisms. Tools that unify customer data—such as customer data platforms (CDPs) or data integration services like Segment—can help ensure that no critical touchpoints are missed, providing a clearer picture of how customers move through the sales funnel.
Influence of Offline and Organic Channels
Attribution challenges don’t end with digital interactions. Offline touchpoints and organic channels can also play significant roles in a customer’s journey, yet they are notoriously difficult to track and attribute properly. For example, a customer may see your product at a physical store, hear about it through word-of-mouth, or encounter an outdoor ad before deciding to make an online purchase. These offline interactions may be critical in driving conversions but are often invisible to traditional digital tracking systems.
Organic channels—like direct traffic, organic search, or word-of-mouth recommendations—pose their own set of attribution difficulties. While it’s easier to track organic search or website traffic, understanding the influence of word-of-mouth and non-digital engagement is much more complex. If a customer learns about your product from a friend and later visits your site directly to make a purchase, attributing that sale correctly becomes a challenge.
Additionally, offline marketing efforts—such as print ads, events, or in-store promotions—can heavily influence online buying behavior, but tracking their impact is difficult without specific tactics in place. For example, QR codes or special URLs can be used in offline ads to link to online campaigns, but they don’t always capture the complete influence of the offline experience on the buying decision.
To mitigate these challenges, businesses need to employ creative attribution strategies. Tracking mechanisms such as unique coupon codes, QR codes, or dedicated landing pages can help measure the effectiveness of offline marketing efforts and organic referrals. Surveys or post-purchase questions asking customers how they heard about the product can also help fill in the gaps, providing more context for the offline interactions that influence online purchases.
Best Practices for Effective Marketing Attribution
Accurate marketing attribution is key to understanding which channels and strategies are driving the most value for your e-commerce business. By following these best practices, you can create a robust attribution system that provides actionable insights, enabling you to optimize your marketing efforts and improve ROI.
Choose the Right Attribution Model
Selecting the right attribution model is one of the most important decisions you’ll make in setting up an effective marketing attribution strategy. There’s no one-size-fits-all model; the right choice depends on your business goals, the length of your sales cycle, and the customer journey specific to your product or service.
- First-Click Attribution: This model gives full credit to the first interaction a customer has with your brand. It’s useful if you want to measure the effectiveness of your awareness campaigns, but it may undervalue touchpoints that happen closer to the purchase.
- Last-Click Attribution: Last-click attribution assigns full credit to the final interaction before the purchase. While popular, it often misses the contribution of earlier touchpoints that may have influenced the buyer’s decision.
- Linear Attribution: This model evenly distributes credit across all touchpoints in the customer journey. It’s a balanced approach that acknowledges every interaction, but it might not fully capture the weight or importance of more critical touchpoints.
- Time Decay Attribution: This model gives more credit to touchpoints that happen closer to the time of conversion. It’s particularly useful for long sales cycles where earlier touchpoints are still important but not as critical as those closer to the purchase.
- Position-Based (U-Shaped) Attribution: The U-shaped model assigns more weight to the first and last touchpoints, while distributing the remaining credit to interactions in the middle. This is ideal for businesses that rely heavily on lead nurturing and want to emphasize the importance of both awareness and conversion-driving touchpoints.
Choosing the right attribution model requires an understanding of your customer’s buying journey and the role each touchpoint plays. E-commerce businesses with shorter sales cycles might prefer last-click attribution, while those with longer, multi-touch journeys may benefit from a multi-touch attribution model like linear or U-shaped.
Consolidate Data Across Channels
For effective attribution, it’s essential to consolidate data from all marketing channels. This means integrating data from paid ads, email marketing, social media, organic search, affiliate programs, and even offline marketing efforts. Without a unified view of customer interactions across these channels, you risk losing critical insights that could affect how you evaluate your marketing efforts.
Consolidating data allows you to track the complete customer journey and ensures that no touchpoint is overlooked. Tools like Google Analytics, HubSpot, or customer data platforms (CDPs) can help unify your marketing data, providing a holistic view of how customers move through different stages of the funnel. This integration also helps avoid attribution gaps that could arise from siloed data systems.
By having all your data in one place, you can make more informed decisions about where to invest your marketing resources. For example, you may find that while paid ads drive a lot of initial awareness, email marketing is more effective at nurturing leads and driving final conversions.
Regularly Review and Adjust Attribution Models
Attribution isn’t a one-time task; it should be an ongoing process that evolves with your business. Customer behaviors, market conditions, and marketing channels change over time, and your attribution models need to reflect these shifts.
For example, you may notice that customer journeys have become longer or more complex, involving multiple touchpoints across different channels. In this case, you might need to shift from a last-click model to a multi-touch model to better understand the full customer journey. Alternatively, if a new marketing channel starts driving significant traffic or conversions, you may need to adjust your model to account for its growing impact.
By regularly reviewing your attribution data, you can spot trends or inefficiencies and make adjustments accordingly. Monitoring how your attribution models perform over time ensures that you’re always working with the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Prioritize Multi-Touch Attribution
Moving beyond last-click attribution is essential if you want to understand the full impact of your marketing efforts. Last-click models often overvalue the final touchpoint while undervaluing earlier interactions that contribute to a customer’s decision to purchase.
Multi-touch attribution models distribute credit across multiple touchpoints, providing a more nuanced view of how each channel contributes to the overall journey. By prioritizing multi-touch attribution, you can see how different channels work together to drive conversions. For example, you might discover that a social media ad drives a lot of traffic but rarely leads directly to a sale—however, it plays a key role in raising awareness and setting up the conversion that happens later through an email campaign or direct search.
Multi-touch attribution allows you to optimize your marketing efforts by understanding which combinations of channels are most effective, rather than relying solely on the last interaction.
Implement Proper UTM Tracking
UTM (Urchin Tracking Module) parameters are a critical part of any effective attribution strategy. These simple snippets of text added to the end of your URLs allow you to track the performance of your marketing campaigns in detail, ensuring accurate attribution across channels.
UTM parameters typically track five key elements: source, medium, campaign, term, and content. By using these parameters consistently, you can capture detailed data about how customers arrived at your website. For example, if you’re running a Facebook ad campaign, adding UTM parameters to your URLs helps you see exactly how much traffic and how many conversions came from that specific campaign, versus traffic coming from organic social media or other sources.
To make the most of UTM tracking:
- Consistency is Key: Ensure that UTM parameters are used consistently across all campaigns and channels. This avoids confusion and ensures that data is categorized correctly in your analytics tools.
- Track Specific Campaigns: Use descriptive names for campaigns, sources, and mediums, so you can quickly identify where traffic is coming from and how it performs.
- Analyze the Data: Regularly review the performance of campaigns with UTM tracking to measure their effectiveness and make data-driven adjustments.
By implementing UTM parameters correctly, you ensure that all of your marketing touchpoints are accurately tracked, leading to better insights and more precise attribution.
Top Tools for Marketing Attribution in E-commerce
Choosing the right tools for marketing attribution can help e-commerce businesses accurately track customer journeys, understand channel contributions, and optimize marketing performance. Here are some of the top tools that offer robust attribution capabilities specifically tailored to e-commerce.
Google Analytics
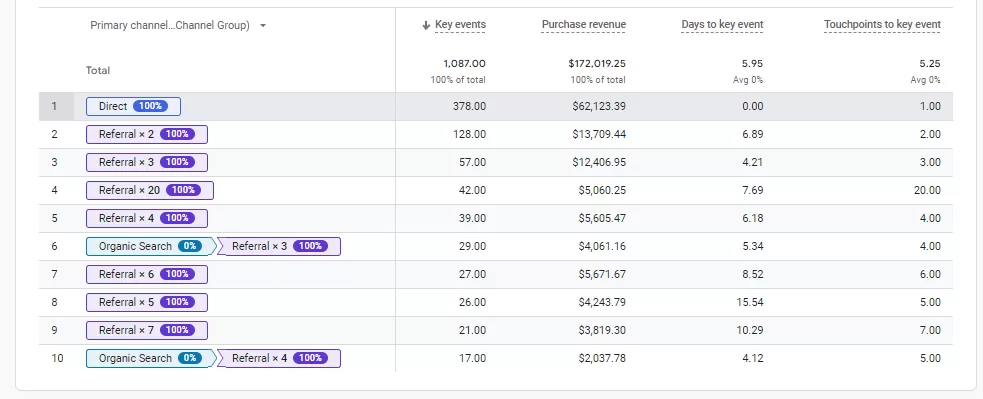
Google Analytics is one of the most widely used tools for tracking website traffic and conversions, and it also offers strong attribution capabilities through its Multi-Channel Attribution Paths and Attribution Models with two possibile views: last non-direct click and data-driven. These features allow businesses to track the sequence of interactions (touchpoints) that lead to conversions, enabling a better understanding of how various channels contribute to sales.
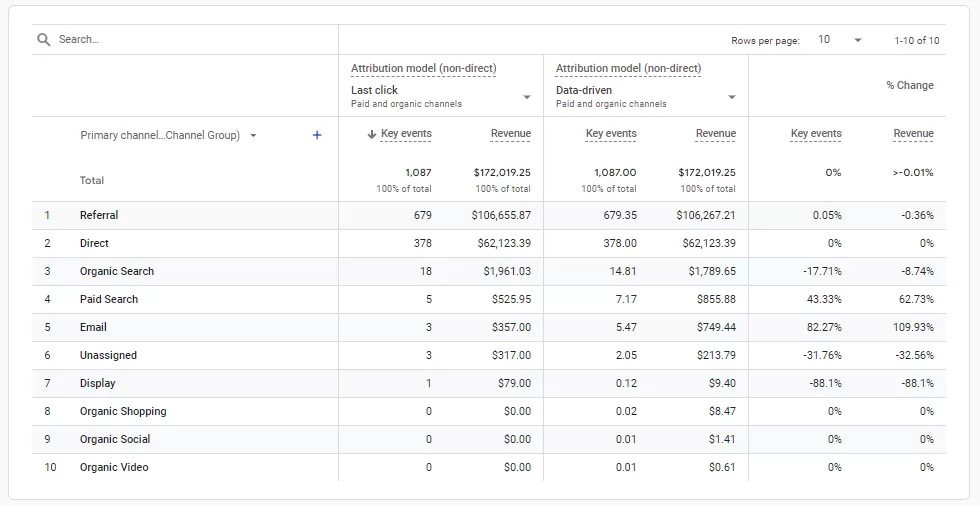 Google Analytics’ built-in attribution tools are especially helpful for businesses looking for an all-in-one platform to track performance across digital channels, making it an essential tool for most e-commerce businesses.
Google Analytics’ built-in attribution tools are especially helpful for businesses looking for an all-in-one platform to track performance across digital channels, making it an essential tool for most e-commerce businesses.
HubSpot
HubSpot is a powerful CRM and marketing automation platform that offers detailed attribution tracking across multiple marketing channels. By combining CRM data with marketing activity, HubSpot provides a holistic view of customer interactions, from the first touch to the final conversion.
HubSpot’s integration of marketing, sales, and customer data provides e-commerce businesses with clear insights into the entire funnel, allowing them to optimize campaigns across channels, from email marketing to paid ads.
Wicked Reports
Wicked Reports is designed specifically for e-commerce businesses, providing detailed, data-driven insights into customer journeys and revenue attribution. It focuses on connecting marketing efforts with actual sales, giving businesses clear data on how marketing campaigns impact revenue over time.
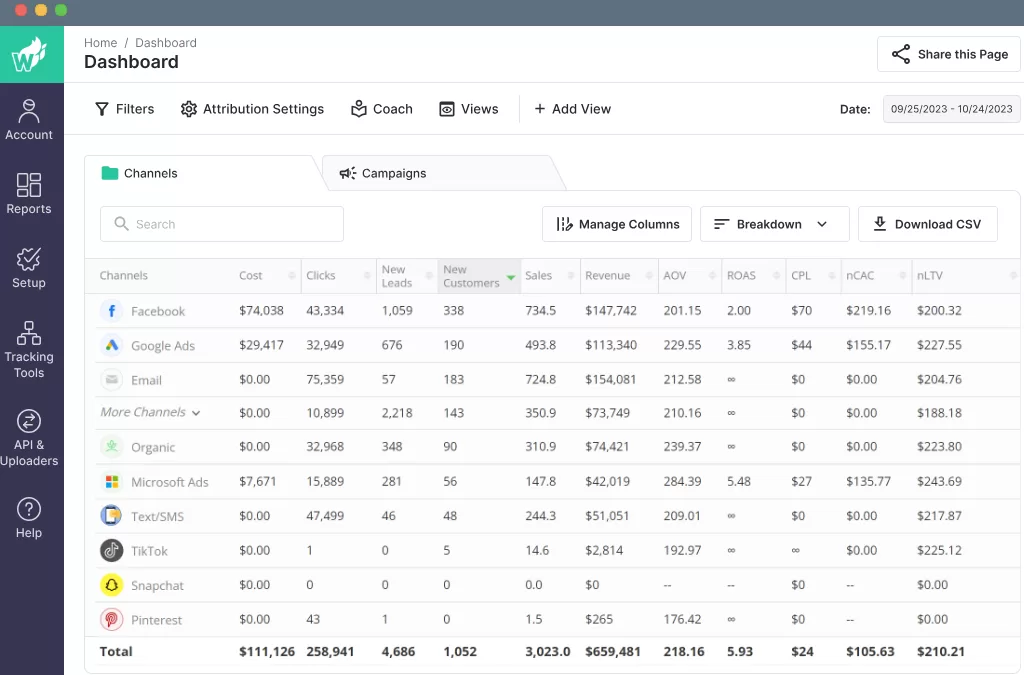 With its focus on long-term data and revenue-driven insights, Wicked Reports is a valuable tool for e-commerce businesses looking to attribute marketing spend more accurately and maximize ROI.
With its focus on long-term data and revenue-driven insights, Wicked Reports is a valuable tool for e-commerce businesses looking to attribute marketing spend more accurately and maximize ROI.
Segment and Data Integration Platforms
Segment is a customer data platform (CDP) that helps businesses unify customer data from multiple sources, making it easier to attribute sales and track customer journeys across channels. By integrating data from tools like Google Analytics, HubSpot, Facebook, and e-commerce platforms, Segment provides a comprehensive view of customer interactions.
- Data Unification: Segment consolidates data from various marketing tools, ensuring that businesses have a single source of truth for all customer interactions. This unified data makes it easier to perform accurate attribution across multiple platforms.
- Cross-Tool Attribution: Segment allows businesses to sync data across different analytics and attribution tools, ensuring that all touchpoints—whether from social media, paid search, email, or direct traffic—are accurately tracked.
By centralizing customer data, Segment enables e-commerce businesses to create more complete attribution models, ensuring that no touchpoint is overlooked in the customer journey.
Measuring the Impact of Marketing Attribution
Tracking Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
Accurate attribution is critical for measuring Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) in e-commerce. ROAS calculates the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising, and having clear attribution data allows businesses to understand how each marketing channel contributes to the bottom line. When the attribution model correctly allocates credit to various touchpoints along the customer journey, businesses can see which channels or campaigns deliver the highest returns. For example, with multi-touch attribution, businesses can evaluate how a combination of paid social ads and email marketing drives conversions rather than just the final touchpoint. This leads to a more accurate calculation of ROAS, allowing businesses to optimize their ad spend and focus on the most profitable channels.
Budget Allocation Based on Attribution Insights
Attribution data plays a vital role in helping businesses allocate their marketing budget more efficiently. By understanding which channels contribute the most to conversions and customer acquisition, businesses can make informed decisions about where to invest their resources. If attribution data reveals that paid search is driving more initial traffic, but social media ads are playing a crucial role in closing sales, businesses can redistribute their marketing budget to amplify the efforts that are working at each stage of the funnel. This strategic allocation ensures that resources are being used where they will have the greatest impact, leading to higher returns on investment and improved campaign performance.
Optimizing Campaigns Based on Attribution Data
Attribution data offers a wealth of insights that can help businesses tweak and optimize their campaigns. For instance, if multi-touch attribution shows that certain channels are contributing more in the awareness phase of the customer journey, marketers can refine their messaging for those channels to drive even more top-of-funnel engagement. Conversely, if a campaign is performing well in the middle of the funnel but failing to convert, businesses can adjust their bottom-funnel tactics, such as refining call-to-actions or offering discounts. Continuous monitoring and optimization based on attribution data help ensure that each campaign delivers maximum value by focusing on the areas that need improvement.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Over-Reliance on Last-Click Attribution
One of the most common pitfalls in marketing attribution is over-reliance on last-click attribution. While easy to implement, last-click attribution can be misleading because it only gives credit to the final touchpoint before conversion. This model undervalues earlier interactions that may have played a crucial role in nurturing the customer, such as initial awareness or mid-funnel engagement. Relying solely on last-click data can lead businesses to mistakenly invest in channels that appear to drive conversions but are only reaping the benefits of work done by other channels earlier in the journey. To avoid this, businesses should prioritize multi-touch attribution, which distributes credit across all relevant touchpoints, providing a more comprehensive view of how different channels work together to drive conversions.
Ignoring Offline and Cross-Device Contributions
Another pitfall is failing to account for offline interactions and cross-device activity. In today’s multi-device, multi-channel world, customers may engage with a brand in person, switch between devices, and still complete the purchase online. Ignoring these touchpoints in attribution models can result in a skewed view of performance. For instance, a customer might discover a product in-store, research it on their phone, and then buy it later from their desktop. Without tools that track these behaviors, such as QR codes or cross-device tracking solutions, businesses risk undervaluing the role of offline and mobile interactions. Ensuring that your attribution strategy captures both offline and online touchpoints is critical for creating a true picture of the customer journey.
Data Privacy and Tracking Limitations
As privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA become more widespread, businesses face growing challenges in tracking user activity and collecting data. Restrictions on the use of third-party cookies, increased cookie blocking, and opt-in requirements for data collection all limit the ability to track customer journeys accurately. To navigate these challenges, businesses need to adopt privacy-compliant solutions like first-party data tracking, server-side tagging, and clear consent mechanisms. Additionally, developing trust with users through transparent data practices can help mitigate the impact of privacy regulations on attribution efforts.
Future Trends in Marketing Attribution for E-commerce
AI and Machine Learning in Attribution
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are playing an increasingly important role in marketing attribution, allowing businesses to predict outcomes and generate insights from vast amounts of data. AI-driven attribution models can analyze patterns in customer behavior across multiple touchpoints and assign credit more accurately by learning from historical data. These models can also adapt to changes in customer behavior, providing more dynamic attribution that evolves as marketing strategies shift. For example, AI models might detect that a certain combination of channels works particularly well for specific customer segments, helping businesses optimize their campaigns accordingly.
Attribution in a Cookieless World
With the decline of third-party cookies and the shift towards a cookieless world, businesses need to adapt their attribution models. Many traditional tracking methods rely on cookies to follow users across websites and devices, but as privacy concerns grow, businesses are moving towards first-party data and other tracking solutions. Tools like server-side tagging, where data is sent directly from a business’s server rather than relying on the user’s browser, can help maintain accurate attribution without relying on cookies. Investing in solutions that prioritize first-party data, like loyalty programs or gated content that captures user information with consent, will also be crucial for attribution in the cookieless future.
Customer-Centric Attribution Models
As marketing becomes more focused on customer retention and lifetime value (LTV), there’s a growing shift towards customer-centric attribution models. Rather than attributing value based on individual transactions, these models focus on the long-term relationship with the customer, assessing how different marketing channels and touchpoints contribute to building customer loyalty and increasing lifetime value. For instance, an email campaign might not directly lead to an immediate purchase but could play a vital role in keeping a customer engaged with the brand over time. Customer-centric attribution models help businesses prioritize the channels and strategies that contribute to overall customer satisfaction and long-term growth, making them a powerful tool for businesses looking to build enduring customer relationships.
Final Words
Marketing attribution is an essential component of any e-commerce strategy, helping businesses understand how different channels contribute to conversions and customer acquisition. By adopting the right attribution model, consolidating data across platforms, and regularly adjusting strategies based on data insights, e-commerce businesses can make smarter, data-driven decisions that optimize their marketing efforts. Avoiding common pitfalls like over-reliance on last-click attribution and neglecting offline and cross-device touchpoints ensures that every step of the customer journey is accurately captured. As privacy regulations evolve and the digital landscape shifts towards a cookieless future, staying adaptable with tools like AI-driven attribution and customer-centric models will help businesses remain competitive. In a world where every touchpoint matters, effective marketing attribution is the key to maximizing ROI and driving sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is marketing attribution in e-commerce?
Marketing attribution in e-commerce is the process of identifying and assigning credit to the different marketing touchpoints that contribute to a customer’s purchase. It helps businesses understand which channels and strategies are driving sales and customer acquisitions.
Why is multi-touch attribution important for e-commerce businesses?
Multi-touch attribution allows e-commerce businesses to understand how different marketing channels work together to drive conversions. It provides a more holistic view of the customer journey, ensuring that all touchpoints, not just the last one, are given proper credit.
How does marketing attribution improve return on ad spend (ROAS)?
Marketing attribution helps improve ROAS by accurately tracking how different marketing channels contribute to conversions. By understanding the full customer journey, businesses can allocate their ad spend more effectively to the most impactful channels, resulting in higher returns.
What are some common pitfalls in marketing attribution?
Common pitfalls include over-reliance on last-click attribution, ignoring offline and cross-device touchpoints, and data privacy limitations. These issues can lead to incomplete or inaccurate attribution, causing businesses to misallocate their marketing budgets.
How can businesses adapt to attribution in a cookieless world?
As third-party cookies become less reliable, businesses can adapt by using first-party data, implementing server-side tagging, and prioritizing consent-based tracking methods to maintain accurate attribution and improve customer trust.



